Experts divide leukemia into four large groups, each of which can be Acute, which is a rapidly progressing disease that results in the accumulation of immature, useless cells in the marrow and blood, or Chronic, which progresses more slowly and allows more mature, useful cells to be made. In other words, acute leukemia crowds out the good cells more quickly than chronic leukemia.
Lymphocytic and Myelogenous
Leukemias are also subdivided into the type of affected blood cell. If the cancerous transformation occurs in the type of marrow that makes lymphocytes, the disease is called lymphocytic leukemia. A lymphocyte is a kind of white blood cell inside your vertebrae immune system. If the cancerous change occurs in the type of marrow cells that go on to produce red blood cells, other types of white cells, and platelets, the disease is called myelogenous leukemia.
To recap, there are two groups of two groups - four main types of leukemia, as you can see in the illustration below:
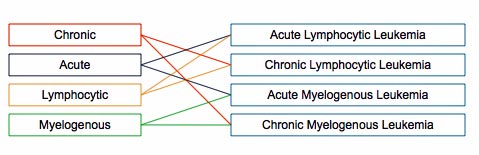
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) - This is the most common type of leukemia among young children, although adults can get it as well, especially those over the age of 65. Survival rates of at least five years range from 85% among children and 50% among adults. The following are all subtypes of this leukemia: precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia, precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Burkitt's leukemia, and acute biphenotypic leukemia.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) - This is most common among adults over 55, although younger adults can get it as well. CLL hardly ever affects children. The majority of patients with CLL are men, over 60%. 75% of treated CLL patients survive for over five years. Experts say CLL is incurable. A more aggressive form of CLL is B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia.
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML - AML is more common among adults than children, and affects males significantly more often than females. Patients are treated with chemotherapy. 40% of treated patients survive for over 5 years. The following are subtypes of AMS - acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia.
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) - The vast majority of patients are adults. 90% of treated patients survive for over 5 years. Gleevec (imatinib) is commonly used to treat CML, as well as some other drugs. Chronic monocytic leukemia is a subtype of CML.



No comments :
Post a Comment